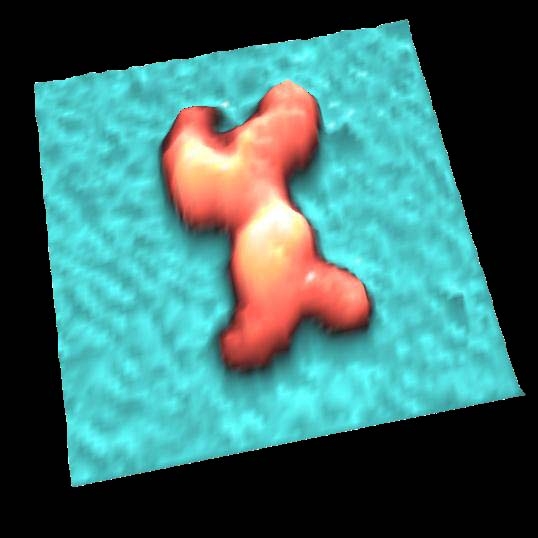
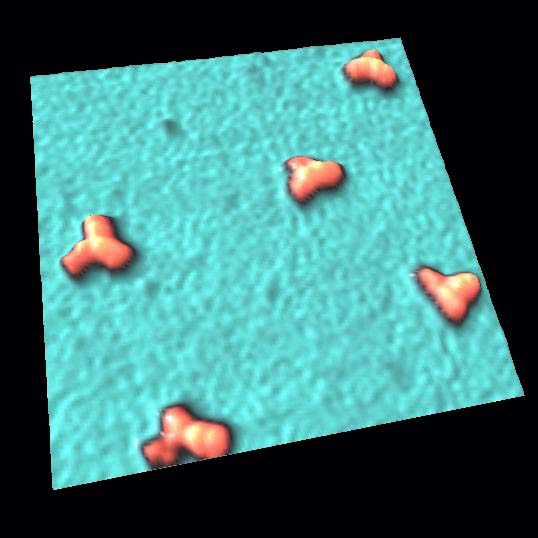
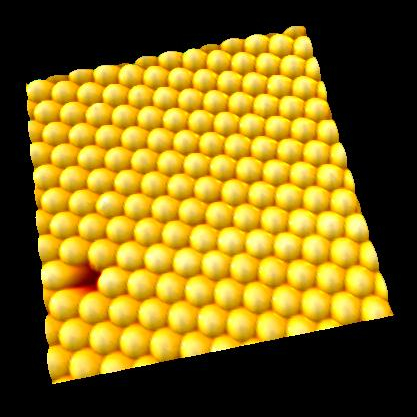
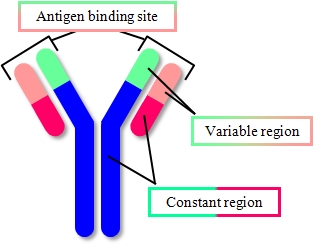
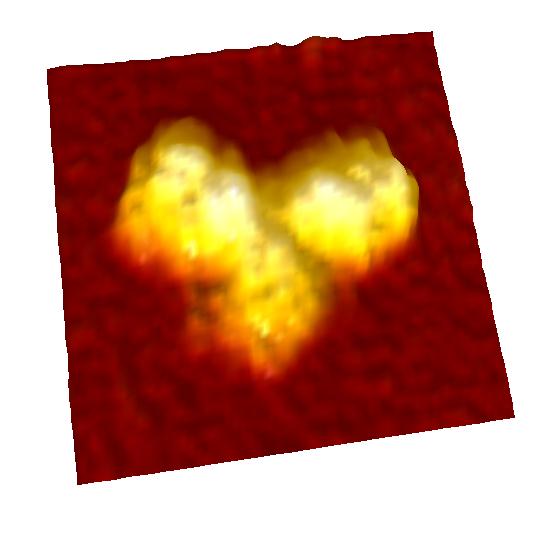
IgG antibodies
0.5 frame / sec. (4 x)
Antibodies (IgG) were observed in solution.
IgG showed "Y"shape and two Fab regions were distinguished clearly.
Because of weak anchoring, IgG keeps its antigen-binding capacity.
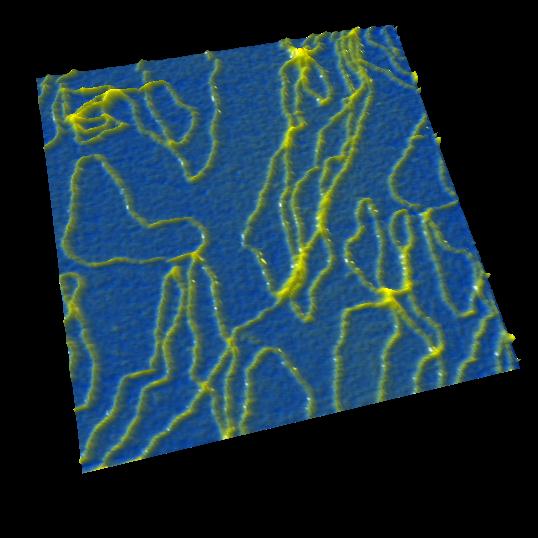
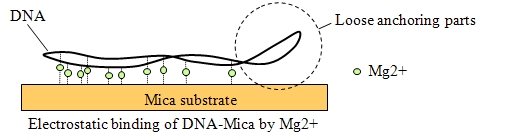
 |
 |
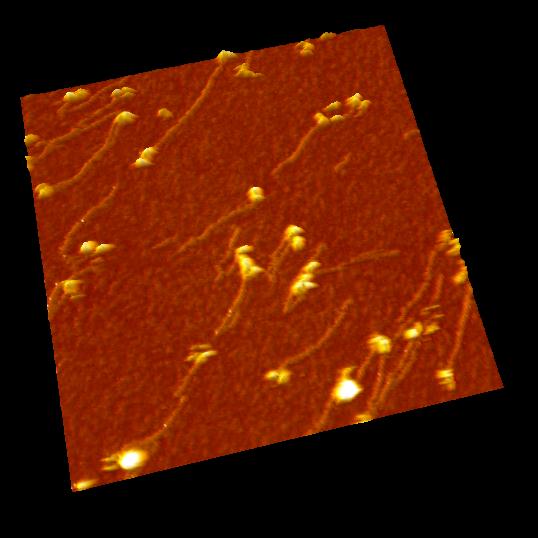
Plasmid DNA
Image of DNA molecules appeared swaying in conventional AFM when without strong anchoring.
However, strong anchoring may diminish true structure and behavior.
With HS-AFM, the structure and movement of plasmid were imaged clearly without strong anchoring.
DNA digestion by endonuclease: DNase I
Scan speed: 1 frame /sec. (30 x)
DNase I is an endonuclease which digests DNA randomly. The arrows in the movie show the parts where DNase I digest DNA.
Please refer the movie of exonuclease Bal31 which digests from end of DNA.
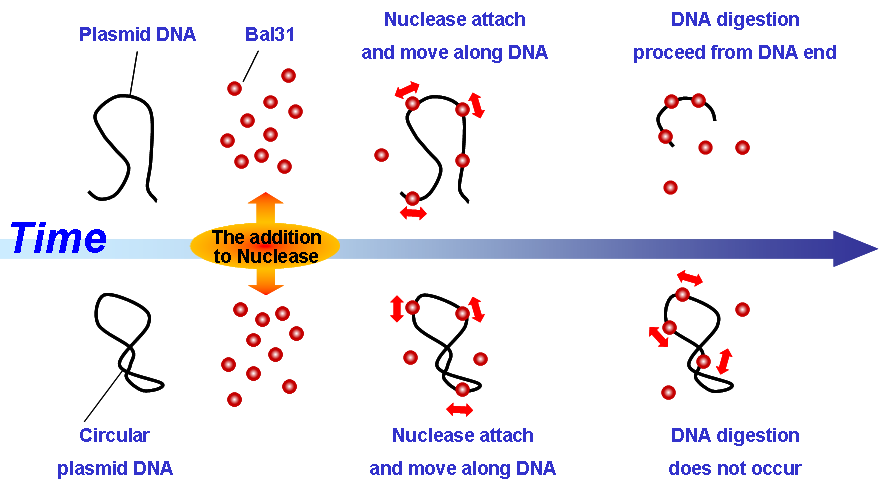
DNA digestion by exonuclease: Bal31
Scan speed: 1 frame / sec. (30 x)
Bal31 is an exonuclease which digests DNA from the end of strand.
Movie show the activity of Bal31 moving along DNA and gradually digest from the ends of DNA chain.
Finally, DNA molecules were digested completely, but circular DNA was not digested. High light dots were Bal31 molecules and they bind to the various positions of DNA.
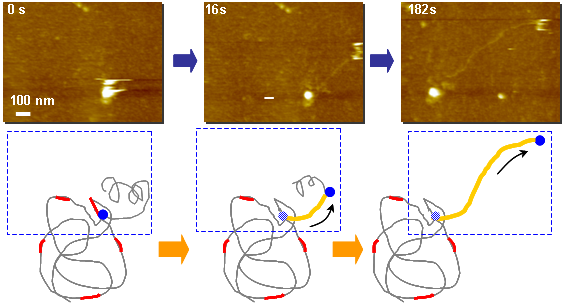
DNA elongation by DNA polymerase: Phi29
Scan Size: 1000 nm × 750 nm
1 frame / sec. (8 x)
Double-stranded DNA(Yellow) is elongated as time passes. Single-stranded λDNA as a mold is fixed on the substrate.
As starting from random hexamer primer(Red) bind to the λDNA mold, phi29 polymerase(Black) synthesize the complementary DNA using dNTP as substrate.
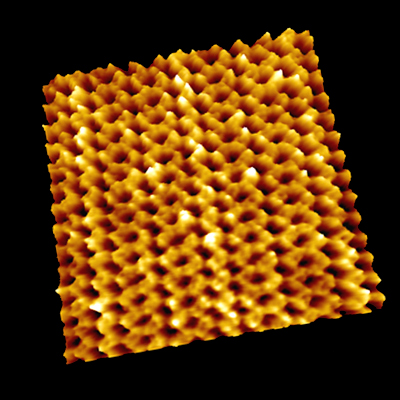
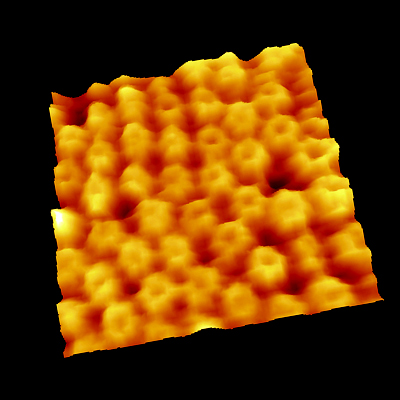
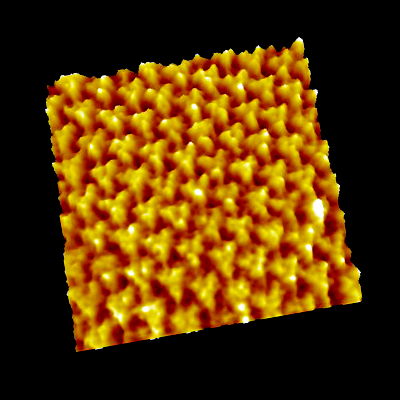
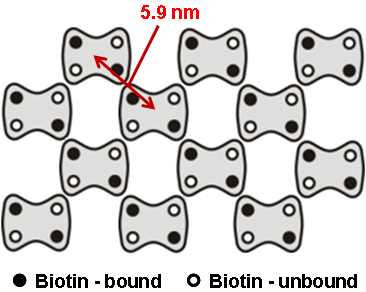
Point defects in streptavidin 2D crystal
The diffusion of point defects in the crystal was successfully observed.
From images, the trajectory tracking of two monovacancy defects was obviously anisotropic with respect to the two axes of the crystalline lattice.
[ Page Top ]
[ Page Top ]
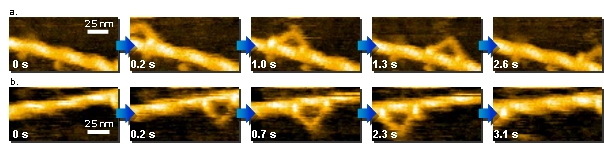
a. and b. : Direct observation of walking myosin V. a. 130 nm x 65 nm, b. 125 nm x 62.5 nm.
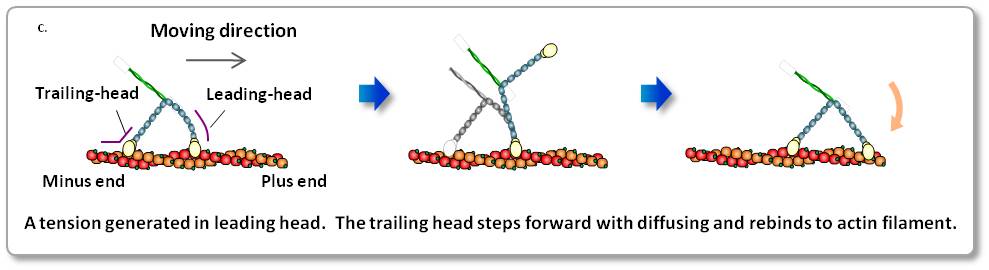
c. Scheme of myosin V walking.
Myosin V is a two-headed processive motor and functions as cargo transporter in cells.
The dynamic behaviors of myosin V translocating along actin filaments were visualized by HS-AFM.
The high-resolution movies provided not only ‘visual evidence’ for previously speculated or demonstrated molecular behaviors, including lever-arm swing, but also more detailed behaviors of the molecules, leading to a comprehensive understanding of the motor mechanism.
This direct and dynamic high-resolution visualization is a powerful new approach to studying the structure and dynamics of biomolecules in action.
N. Kodera et al. Nature 468, 72 (2010). Kanazawa University
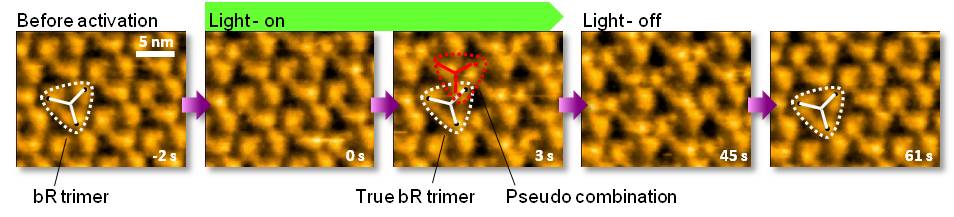
Structural change of bacteriorhodopsin (bR), which is known as light-driven proton pump, has been visualized by HS-AFM. The purple membrane composed of D96N bR mutant, which has a longer photocycle (10’s) than that of the wild type, was adsorbed on mica substrate. Upon illumination with green light (532nm), bR drastically changes its structure and returns to the unphotolysed state in a few seconds after light-off. This outcome is reproducible in repeated dark illumination cycles.
M. Shibata et al. Nature Nanotech. 5, 208 (2010). Kanazawa University
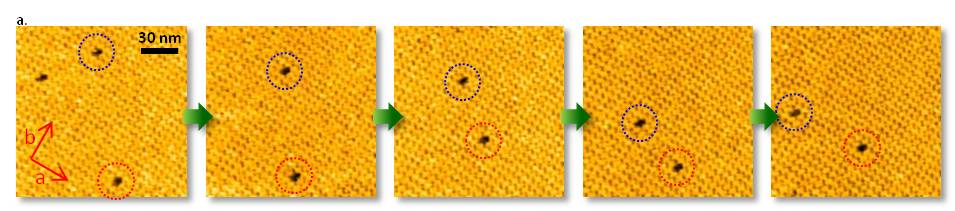
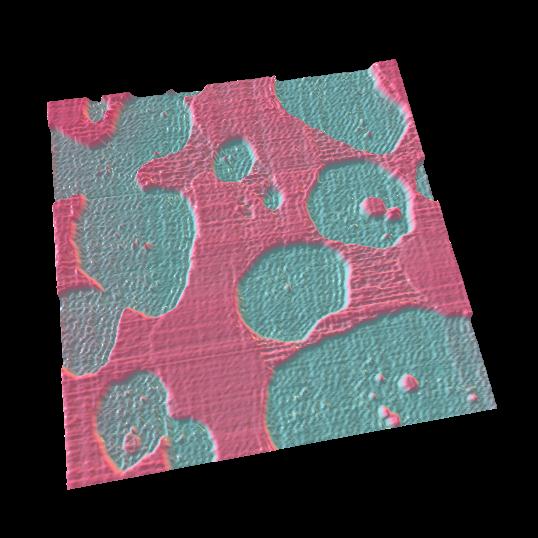
a. Dynamic observation of the diffusion of point defects.
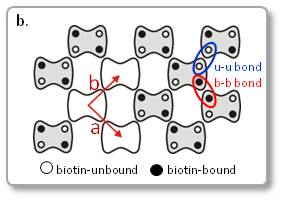
b. Scheme of streptavidin arrays in a C222 crystal. Unit lattice vectors are indicated by red arrows.
The diffusion of point defects in the crystals was successfully observed by HS-AFM.
In Figure a, the trajectory tracking of two monovacancy defects was obviously anisotropic with respect to the two axes of the crystalline lattice.
As a result, the diffusion constant D along each axis could be established to be Da = 20.5 nm2/s and Db = 48.8 nm2/s. This means, HS-AFM is useful for studying various dynamic process, such as the crystal growth and disintegration processes.
D. Yamamoto et al. Nanotechnology 19, 384009 (2008). Kanazawa University
[ Page Top ]
[ Page Top ]